In this article we are going to describe the implementation of Windows Update for Business in substitution of Windows Update Service formerly know as WSUS. So will focuses how to implement it , and how to mitigate the traffic overload passing with Delivery Optimization used by WUfB.
The WUfB is controlled by a GPO that is locate in Computer Configuration => Administrative Templates => Windows Components => Windows Update => Windows Update for Business
Type of updates managed by WUfB :
| Quality updates | contain security, critical, and driver updates. (Released typically on the second Tuesday of each month) |
| Feature updates | contain significant feature additions and changes. (Released as soon as possible) |
To avoid any problems, it’s a best practices to implement some groups, called “rings” as the fallowing example:
- Ring 1 => TESTING
- This member will receive the Semi-Annual Channel Targed
- When quality updates are received? 0 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- When Feature Updates are received? 0 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- Could paused? no
- Ring 2 => PILOT
- This member will receive the Semi-Annual Channel Targed
- When quality updates are received? 10 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- When Feature Updates are received? 10 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- Could paused? no
- Ring 3 => ROLLOUT
- This member will receive the Semi-Annual Channel Targed
- When quality updates are received? 30 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- When Feature Updates are received? 30 days
- Can postpone them for how long? 35 days
- Could paused? no
Understand the “Windows Server servicing channels” used by WUfB .
Basically we have five servicing channels and we can sum-up with this table:
| Channel | How much can deffer? | When? |
| Semi-Annual Channel | 365 days (35 day paused) | When they are declared Semi-Annual Channel about 4 months after Semi-Annual Channel |
| Semi-Annual Channel Targeted | 365 days (35 day paused) | When they are released to the general public |
| Release Preview | 14 days (35 day paused) | Before Microsoft releases them to the general public |
| Preview Build Slow | 14 days (35 day paused) | Receive new builds of Windows before they are available to the general public |
| Preview Build Fast | 14 days (35 day paused) | To participate in identifying and reporting issues to Microsoft |
Managing the bandwidth trought the “Delivery Optimization”
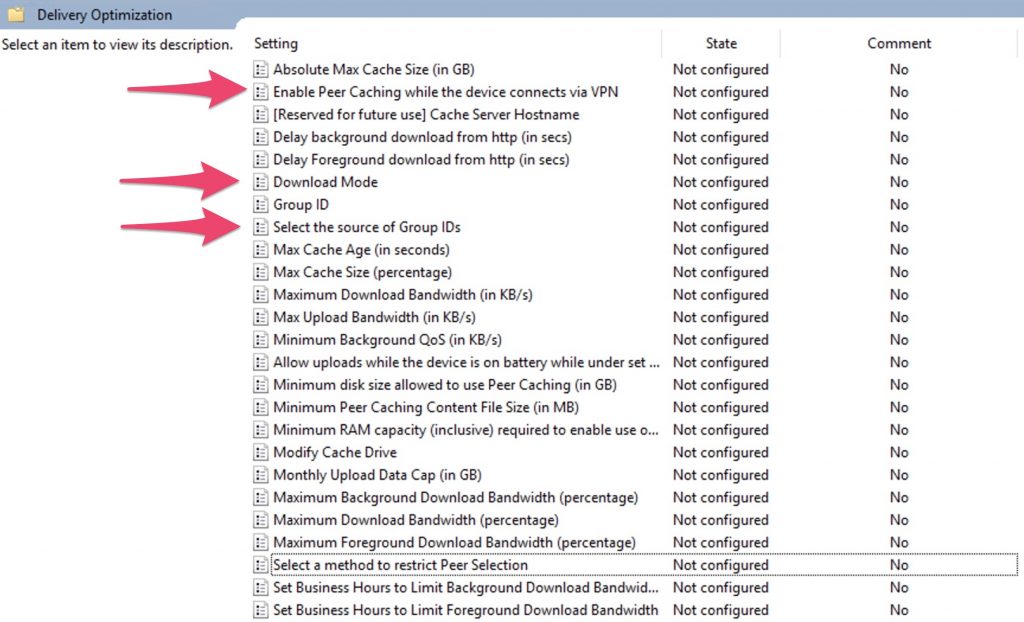
Download Mode
2 = HTTP blended with peering across a private group. Peering occurs on devices in the same Active Directory Site (if exist) or the same domain by default. When this option is selected, peering will cross NATs. To create a custom group use Group ID in combination with Mode 2.
Select the source of Group IDs
Set this policy to restrict peer selection to a specific source.
Options available are:
1 = AD Site.
Enable Peer Caching while the device connects via VPN
Specify “true” to allow the device to participate in Peer Caching while connected via VPN to the domain network.
This means the device can download from or upload to other domain network devices, either on VPN or on the corporate domain network.
if you need, automate the population process of WUfB_ROLLOUT security group . So, before, populate manually the other two groups (WUfB_PILOT and WUfB_TESTING) and use this script to add programmatically other PCs that resides into your AD and have the operative system like Windows 10.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 |
########################################################################### ## Define the AD Sec Group =>>> create them before in your AD... ########################################################################### $Gruppo1 = "WUfB_TESTING" $MembriGruppo1 = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity $Gruppo1 -Recursive | Select -ExpandProperty Name $Gruppo2 = "WUfB_PILOT" $MembriGruppo2 = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity $Gruppo2 -Recursive | Select -ExpandProperty Name $Gruppo3 = "WUfB_ROLLOUT" #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- ############################################################################ # Estracting all PCs objects in AD that is "Enabled" ############################################################################ $tuttipc = Get-ADComputer -filter {Enabled -eq $true } #Counting variable... $a = 0 #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- ############################################################################ # Extracting only Windows 10 pc and add them to WUfB_ROLLOUT ############################################################################ foreach ($pc in $tuttipc) { $pc_all_prop = Get-ADComputer -Identity $pc -property * if ($pc_all_prop.operatingsystem |Select-String -Pattern "Windows 10"){ $pc_all_prop|select name, operatingsystem,Enabled $a +=1 $a ######################################################################## #If the PC is into the "WUfB_TESTING" o "WUfB_PILOT" groups do nothing #----------------------------------------------------------------------- if (($MembriGruppo1 -contains $pc.Name) -or ($MembriGruppo2 -contains $pc.Name)){ write-host $pc.Name " si trova già presente nel gruppo..." -ForegroundColor Green sleep 5 } ######################################################################## #Add the Pc to he PC is into the "WUfB_ROLLOUT" #----------------------------------------------------------------------- else{ write-host "dovrei aggiungerlo al gruppo ROLLOUT ...." -ForegroundColor Magenta Add-ADGroupMember -identity $Gruppo3 –members $pc.Name3 } } else { write-host "do nothing......." } } #----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
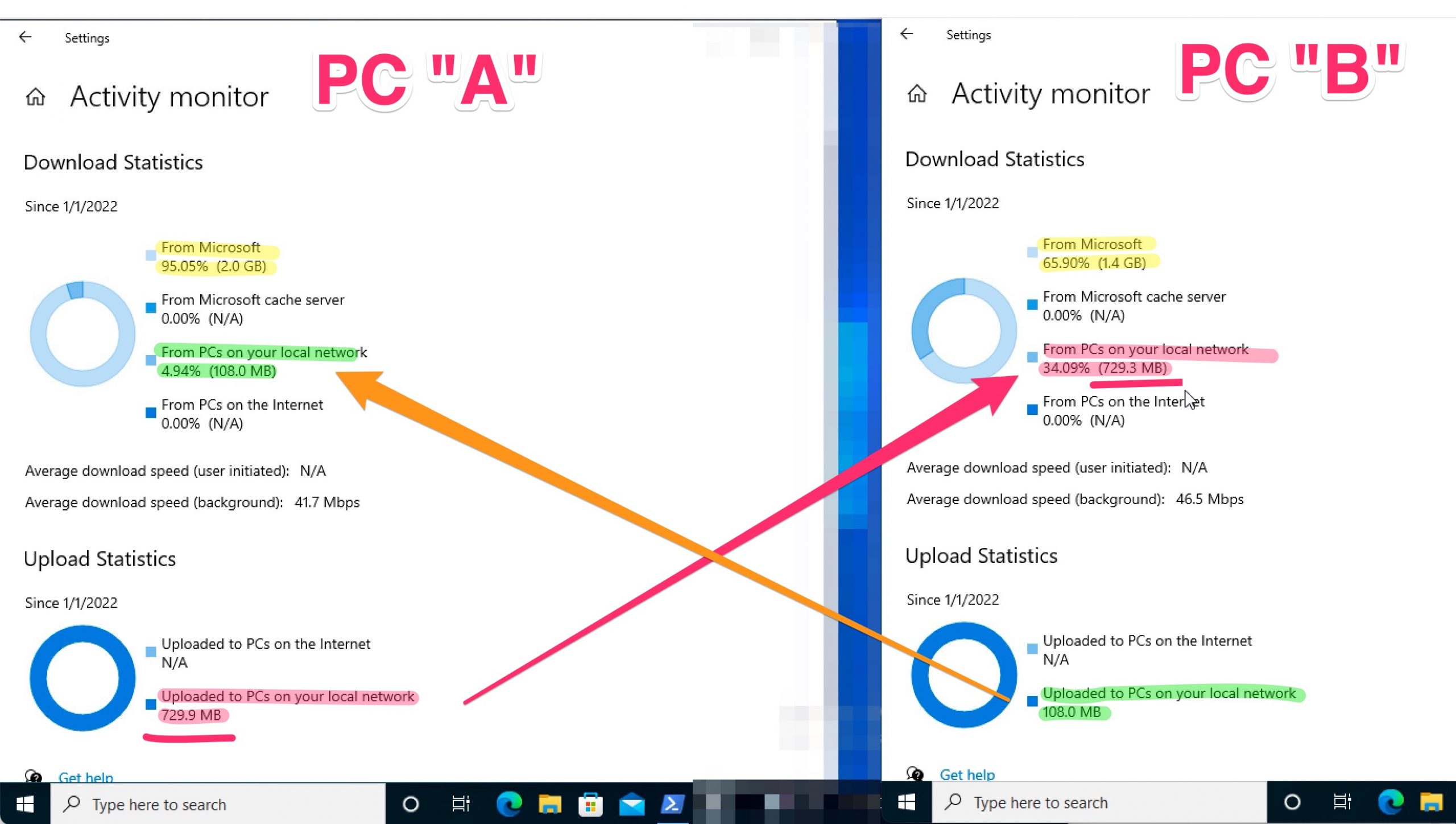
At this point, in my lab , I’ve created two fresh new one Windows 10 to doing some test with this new GPO. The test is simple, I move both this two pcs into the OU that has a GPO as explained before, where i define the WUfB and Delivery Optimization.
After that I’ve launched the Windows Update from PC “A” to populate at least one PC with all updates (remember that WUfB use the PC’s local disk to store the updates that the same pc will deliver to others) . After that, I’ve run W. Updates from the other pc , “B”, to find if this pc use the other as the source of updates.
As you can see, pc “A” has a 95% of updates from internet (Microsoft) but the other, pc “B” has only 65% of updates from Internet and about 34% from local PC. So it Works.